Toyota repurposing used EV batteries into grid-scale renewable energy storage
- PostedPublished 30 December 2023
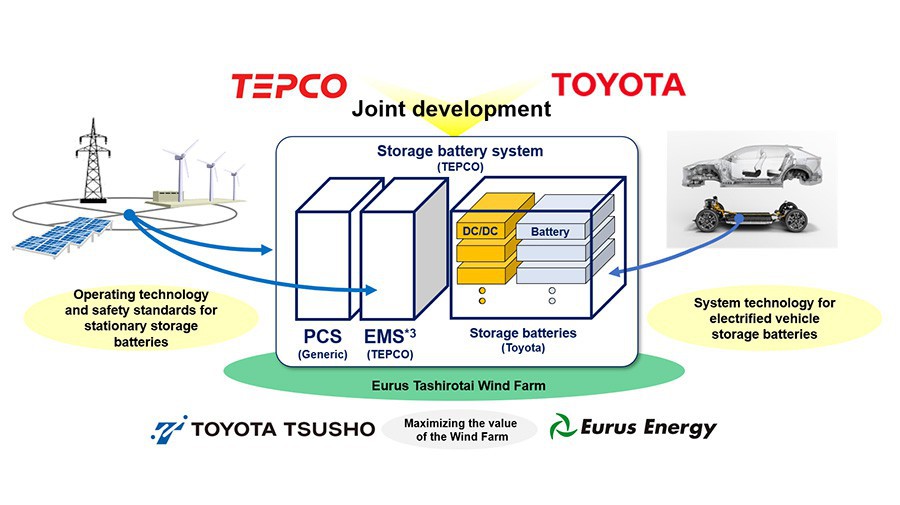
Toyota has partnered with the Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) to create a cutting-edge electric storage system that utilises recycled electric vehicle batteries.
Energy stored in these batteries will come from renewable sources and be used during times when wind-generated power isn’t enough to meet grid requirements. The new electric storage system will have an output of 1MW and a capacity of 3MWh.
Toyota has previously explored the use of electric vehicle batteries to power households; back in 2012, it developed and tested a vehicle-to-home (V2H) system in Japan. This system enabled electric vehicles to supply power to homes during power outages or emergencies. This was part of a larger effort to promote the use of electric vehicles and renewable energy sources.
The Toyota Tsusho Corporation and Eurus Energy Holdings Corporation will install the system at the Eurus Tashirotai Wind Farm, one of Japan’s largest wind power plants. The wind farm contains 33 turbines and can produce enough electricity to power around 60,000 households. It is situated on a former golf course, highlighting how unused land can be repurposed for renewable energy projects.
TEPCO’s commitment to renewable energy and its collaboration with Toyota on this project demonstrates the company’s dedication to creating sustainable and reliable energy solutions for the future. With its extensive experience in the electric power industry, TEPCO is well-positioned to help drive the development of new green technologies.
A collaborative verification project is scheduled to take place later this year to evaluate the system’s operation, performance, and feasibility, determining its commercial viability for further use in the electricity market. This verification process will provide valuable insights into the system’s effectiveness and usability, helping to refine and optimise the technology for future use.
Toyota has been involved in electric vehicle (EV) battery development since the 1990s, and in 1997, the company launched the world’s first mass-produced hybrid vehicle, the Toyota Prius.
Its goal is to create safe, affordable, and high-energy-density batteries to achieve a carbon neutral mobility society while establishing a circular economy that prioritises resource recycling to benefit both the environment and society. By utilising this innovative approach, Toyota is turning a potential waste stream into a valuable resource.
As renewable energy and electrified vehicles become more widespread and the global focus shifts towards CO2 neutrality, the storage battery market is predicted to sustain its rapid growth, which could have a significant impact on the energy storage market.
This is because as more EVs are introduced into the market, the availability of used batteries for energy storage will increase, which would further lower the cost of energy storage systems. This development has the potential to not only create a more efficient and reliable energy system but also lower electricity costs for consumers.
- CategoriesIn Latest News
- TagsBatteries, battery, electric vehicles, EV, Toyota

